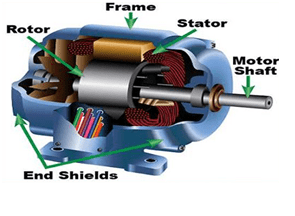
Due to worse effect of fossil fuel on environment, Electric vehicle (EV) was introduced. The core element of the EV, apart from Batteries, which replaces the Internal Combustion engines is an Electric motor. Older designs used standard DC motors, which are relatively economically controlled when driven with batteries. New designs use either AC Induction motors or Permanent Magnet Rotor AC motors, driven by electronic inverters. In general, lower power applications will use the PM AC motors which are slightly more efficient for a given task, while high-performance vehicles will use induction motors since they are capable of very large acceleration torques relative to their weight for short intervals, until they overheat. All new Electric Vehicles and even hybrids use AC electric motors. They are lighter, more powerful and can be used as a generator makes power as you slow down or brake called Regenerative braking.
Permanent Magnet AC Motor
Permanent magnet AC motors (PMAC) are just like standard induction AC motors except they have permanent, rare-earth magnets attached to their rotors. Having these permanent magnets instead of electromagnets reduces energy losses in the motor. They are also called synchronous AC motors. Most of the automotive manufacturers use PMAC motors for their hybrid and electric vehicles. For example, Toyota Prius, Chevrolet Bolt EV, Ford Focus Electric, zero motorcycles S/SR, Nissan Leaf, Hinda Accord, BMW i3, etc use PMAC motor for propulsion.
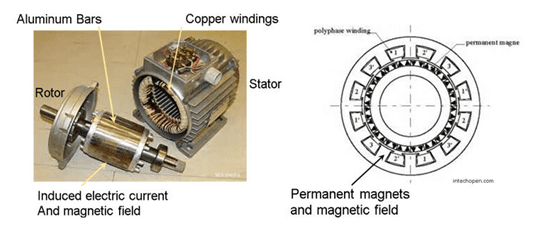
AC Induction Motors
Induction motor works on the principle of induction where electro-magnetic field is induced into the rotor when rotating magnetic field of stator cuts the stationary rotor. Induction machines are by far the most common type of motor used in industrial, commercial or residential settings. Squirrel cage induction motors have a long life due to less maintenance. Induction motors can be designed up to an efficiency of 92-95%. The drawback of an induction motor is that it requires complex inverter circuit and control of the motor is difficult.
Typically, most of the manufacturers use synchronous motors, but whether it is a permanent magnet or electromagnet strongly influences the performance. The key difference is that AC induction motors have to use electricity to generate the magnetic currents inside the motor, which cause the rotor to spin, whereas a permanent magnet motor doesn’t require that additional current since its magnets—created from rare-earth materials—are always “on.”
No comments:
Post a Comment